Last Updated on: 18th December 2024, 12:33 pm
A balanced fitness routine is essential for optimal health and performance. Combining cardio and strength training offers a comprehensive approach to fitness. Misconceptions exist about overtraining or hindering muscle growth, but integrating these elements can enhance cardiovascular health, muscle growth, and endurance.
- The benefits of integrating cardio into your strength training include improved cardiovascular health and muscle endurance.
- This approach can lead to better body composition, increased metabolic rate, and a stronger body.
- Understanding how to blend these elements effectively is key to creating a sustainable routine.
Discover the balance in your fitness routine for rewards like a healthier heart and a more toned physique.
Understanding the Benefits of Cardio in a Strength Routine
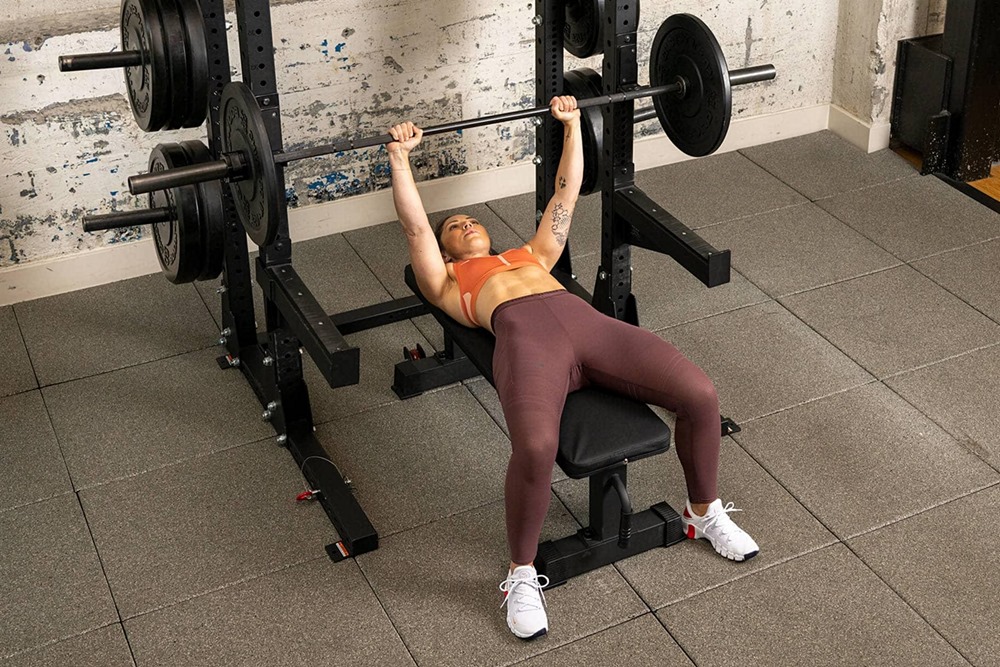

Integrating cardio into a strength training routine enhances comprehensive fitness. The benefits are significant and multifaceted.
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Cardiovascular exercises strengthen the heart and improve blood flow, enhancing oxygen and nutrient delivery to muscles.
- Enhanced Muscle Recovery: Low to moderate intensity cardio facilitates muscle recovery by stimulating blood flow and delivering nutrients to repair muscle tissue.
- Increased Fat Loss: Cardio accelerates fat loss by building muscle and burning calories, key for a leaner physique.
- Boost in Overall Endurance and Performance: Increased stamina allows for harder and longer training, enhancing overall performance.
Integrating cardio into a strength training routine optimizes health, enhances recovery, and maximizes performance. Embrace the synergy for a healthier, stronger you.
Planning Your Integrated Routine for Optimal Results
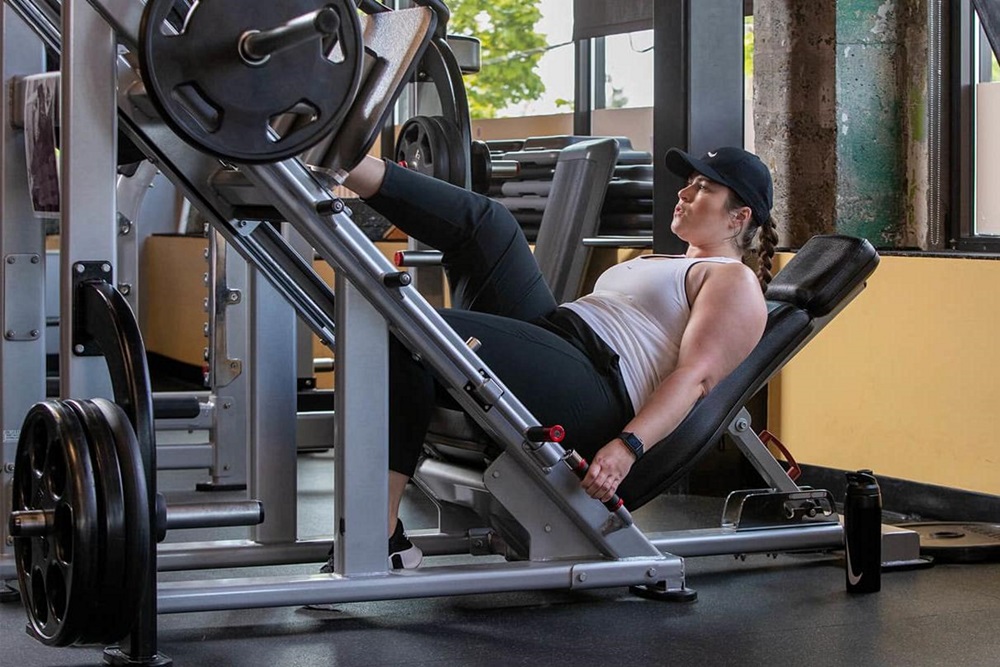

Define your fitness goals, whether building muscle, losing fat, or enhancing endurance. This clarity guides your workout structure.
Perform cardio after strength training to preserve energy for lifting weights, maximizing muscle growth while gaining cardiovascular benefits. Your specific goals might require a different approach.
- Choose between Low-Intensity Steady State (LISS) and High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT).
- LISS, like brisk walking or cycling, is suitable for recovery days.
- HIIT, with intense activity bursts, is effective for fat loss and cardiovascular health.
- Integrate both types, adjusting frequency and intensity to your fitness level and goals.
Strategically integrate cardio into your strength training routine by assessing goals, understanding timing, and selecting appropriate cardio types for optimal results.
Strategies for Combining Cardio and Strength Training Without Overtraining
Blending cardio with strength training requires balancing intensity, volume, and rest. Rest and recovery are crucial to prevent overtraining.
- Overtraining risks include fatigue, decreased performance, insomnia, and increased injury susceptibility. Listen to your body and adjust your routine accordingly.
- Balance intensity and volume by varying workout intensity with volume. After high-intensity strength sessions, opt for low-intensity cardio to aid recovery and enhance endurance.
Integrate cardio into your strength training routine thoughtfully. Pay attention to rest, recognize overtraining signs, and balance workout intensity for a sustainable and effective fitness journey.
Sample Integrated Cardio and Strength Training Plans

Blend cardio with strength training for comprehensive health benefits. Tailor this blend to your fitness level to ensure progress without overtraining.
Plan for Beginners
Start with two days of full-body strength training using light weights or bodyweight exercises. Add two days of low-intensity cardio, like brisk walking or cycling for 20-30 minutes.
Plan for Intermediate Level
Include three days of strength training, targeting different muscle groups each session. Add moderate-intensity cardio, such as jogging or swimming, for 30-40 minutes on alternate days.
Plan for Advanced Athletes
Engage in four days of strength training with heavier weights and complex movements. Integrate HIIT sessions twice a week to boost cardiovascular health and fat loss.
Adjust workout intensity and volume as you progress to ensure continuous improvement and avoid plateaus.
Nutrition and Hydration: Fueling Your Integrated Training

Proper nutrition and hydration are crucial for recovery and sustained energy in integrated training.
- Carbohydrates replenish glycogen stores.
- Proteins repair and build muscle tissue.
After a workout, a meal rich in both is essential for recovery.
Hydration supports metabolic functions and nutrient transfer, regulating body temperature and lubricating joints.
- Drink water throughout the day, especially around workout times, to meet hydration needs.
Supplements can support training:
- BCAAs may promote muscle synthesis and reduce soreness.
- Beta-alanine and creatine enhance performance in both strength and cardio workouts.
- Omega-3 fatty acids aid in recovery with anti-inflammatory properties.
Supplements should complement, not replace, a nutrient-dense diet.
Integrate cardio into your strength routine with a thoughtful approach to nutrition and hydration for successful workouts and recovery.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Your Routine

Set realistic and measurable goals to track progress. This clarity provides a benchmark for tracking progress.
Keep a detailed log of workouts and achievements to:
- Celebrate victories and track progress.
- Identify when and where adjustments are needed.
Adjusting your routine is a step towards improvement. Listen to your body and respond to its needs.
- Increase cardio intensity or diversify strength exercises as needed.
- Ensure adequate rest if your body signals the need.
Integrate cardio into your strength training routine dynamically. Set realistic goals, track progress, and adapt your approach for ongoing improvement.
Wrapping It Up
Balance breeds strength in fitness. By integrating cardio with strength training, you embark on a journey that challenges yet rewards, pushing boundaries while ensuring sustainable progress. Embrace this holistic approach to unlock unparalleled health and performance.

