Last Updated on: 18th December 2024, 12:35 pm
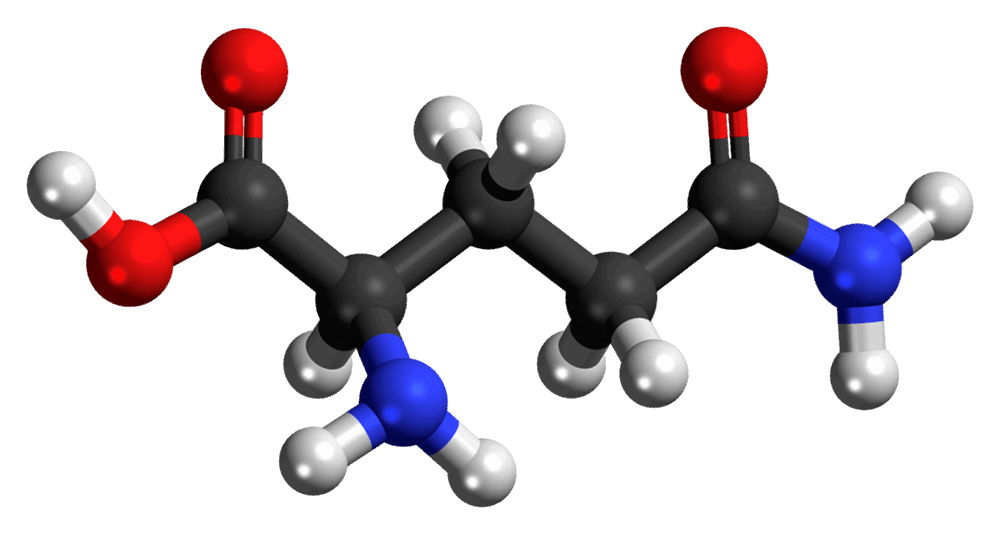
Glutamine, a critical amino acid, plays a pivotal role in our body’s functionality. It’s the most abundant amino acid in the bloodstream, underscoring its significance. This powerhouse supports various essential functions, from immune system fortification to gut health and beyond. Its versatility is unmatched, acting as a building block for proteins and a critical fuel source for immune cells.
- For athletes and those dedicated to regular exercise, glutamine becomes even more crucial.
- It facilitates recovery, reduces muscle soreness, and enhances overall performance.
- When the body is pushed to its limits, glutamine levels can deplete, making supplementation a game-changer for those looking to optimize their recovery and maintain peak performance.
Understanding glutamine’s roles illuminates its undeniable importance in achieving and maintaining optimal health and athletic performance. It’s not just about building muscle; it’s about nurturing a resilient body capable of withstanding and thriving under stress. Glutamine is your ally, whether you’re an athlete striving for excellence or simply someone committed to staying active and healthy.
Understanding How Exercise Affects Glutamine Levels

Intense exercise has a profound impact on glutamine levels in the body. This critical amino acid, abundant under normal conditions, can significantly deplete during prolonged or high-intensity workouts. Such depletion affects both muscle recovery and immune function. The body, in its quest for recovery, demands more glutamine than usual, leading to a shortfall that can hamper the healing process and lower immune defenses.
- Depleted glutamine levels post-exercise are not to be taken lightly.
- They can lead to slower recovery times, increased muscle soreness, and a higher susceptibility to infections.
- Glutamine serves as vital fuel for immune cells and plays a crucial role in the synthesis of proteins necessary for muscle repair and growth.
Research findings underscore the significance of maintaining glutamine levels after strenuous activities. Studies have shown that athletes engaging in intense training often experience a drop in glutamine, which correlates with an increased incidence of upper respiratory tract infections. Furthermore, supplementation with glutamine has been found to enhance recovery and immune function, highlighting its importance in the post-exercise period.
The Role of Glutamine in Exercise Recovery

Glutamine, a key player in the world of fitness, shines brightly when it comes to muscle repair and growth. After a grueling workout, muscles are in dire need of repair. Glutamine steps in, facilitating the synthesis of proteins necessary for muscle recovery. This process not only repairs damaged fibers but also contributes to muscle growth, making glutamine an invaluable ally in the quest for strength and endurance.
- But glutamine’s role extends beyond muscle repair.
- It’s a guardian of the immune system during recovery periods.
- Intense exercise can temporarily weaken the immune system, leaving the body more susceptible to infections.
- Glutamine, however, fuels immune cells, bolstering the body’s defenses during these critical recovery times.
Moreover, glutamine aids in glycogen replenishment, a crucial aspect of recovery. Glycogen, the stored form of glucose, serves as a primary energy source during exercise. Depleted levels post-workout can lead to fatigue and prolonged recovery times. Glutamine’s contribution to glycogen synthesis ensures energy stores are quickly replenished, facilitating a faster return to peak performance.
Supplementation of Glutamine for Enhanced Recovery
Glutamine supplements come in various forms, including powders, capsules, and liquids, catering to different preferences and lifestyles. Each form promises to replenish glutamine levels efficiently, aiding in swift recovery from intense workouts.
- For optimal recovery benefits, the recommended dosage of glutamine ranges from 5 to 10 grams per day.
- Timing is crucial; consuming glutamine immediately post-workout can significantly enhance muscle recovery and immune support.
- An additional dose before bed may further facilitate muscle repair and growth during sleep, when the body’s recovery processes are most active.
Scientific studies shed light on the effectiveness of glutamine supplementation for exercise recovery. Research indicates that glutamine not only accelerates muscle repair but also reduces muscle soreness, allowing athletes to return to training with less downtime. Furthermore, studies highlight glutamine’s role in bolstering the immune system, which is often compromised after strenuous exercise, thereby supporting overall health and resilience.
Dietary Sources of Glutamine and Their Role in Recovery

Natural food sources are abundant in glutamine, offering a variety of options for those looking to maintain adequate levels through diet. Animal proteins such as beef, chicken, and fish are rich in this amino acid, as are dairy products like milk and yogurt. For vegetarians or those seeking plant-based options, beans, peas, and lentils are excellent sources. Additionally, certain nuts and eggs also contribute to glutamine intake, ensuring that everyone has access to this crucial nutrient.
A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in sustaining glutamine levels, crucial for muscle recovery and immune function. Incorporating a diverse range of glutamine-rich foods ensures that the body receives a steady supply, supporting its needs especially after intense physical activity. This approach not only aids in recovery but also contributes to overall health and well-being.
While dietary sources provide a natural way to obtain glutamine, supplementation can offer a concentrated dose, beneficial during periods of increased demand, such as post-exercise recovery. Supplements, however, should complement, not replace, a balanced diet. The benefits of dietary glutamine include its integration with other essential nutrients that support absorption and overall health, something supplements alone cannot fully replicate. Therefore, a combination of both dietary sources and supplementation, when necessary, is often the best strategy for maintaining optimal glutamine levels and supporting recovery.
In conclusion, a diet rich in glutamine from various sources is fundamental for those engaged in regular exercise. It supports not only the recovery process but also enhances immune function and overall health. While supplements can provide an additional boost, they work best in conjunction with a well-rounded diet, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to nutrition and recovery.
Potential Risks and Considerations in Glutamine Supplementation
While glutamine is generally considered safe, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects and contraindications:
- Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating or gas, when taking glutamine supplements.
- In rare cases, allergic reactions can occur, manifesting as a rash or itching.
- Those with kidney or liver disease should exercise caution, as high levels of amino acids can exacerbate these conditions.
Understanding the safe limits of glutamine intake is essential. The body typically tolerates up to 14 grams per day well, but exceeding this amount could lead to adverse effects. It’s important to adhere to recommended dosages and to consider the glutamine obtained from dietary sources to avoid excessive intake.
Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting supplementation is paramount. They can provide:
- Personalized advice based on your health status and fitness goals.
- Important information for those with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications, as glutamine may interact with certain drugs.
Ultimately, while glutamine supplementation can be beneficial for exercise recovery, it should be approached with care. Monitoring your body’s response and adjusting intake as necessary can help mitigate risks, ensuring that glutamine remains a helpful ally in your fitness regimen.
Bringing It All Together
Glutamine powers exercise recovery. It’s the resilience behind your fitness. This amino acid balances the body’s demands, ensuring swift repair and robust immunity. Through dietary sources and supplementation, glutamine supports a journey toward peak performance and health. Embrace its benefits, fueling your path to recovery and beyond.