Last Updated on: 14th July 2024, 09:33 am
Introduction to Yoga for Athletes

Yoga, an ancient practice rooted in over 5,000 years of history, is not just for those seeking a peaceful retreat from the hustle and bustle of daily life. It’s a powerful tool for athletes, offering benefits that extend far beyond the mat. The fusion of strength, flexibility, and mental focus that yoga demands can significantly enhance athletic performance, making it a perfect complement to any training regimen.
As the world of sports evolves, so too does the approach to training and recovery. Incorporating yoga into athletic training is no longer a trend but a staple. Athletes across the globe are turning to yoga not just for its physical benefits, but for its ability to sharpen the mind, improve breathing, and increase body awareness. These elements are crucial for anyone looking to excel in their sport.
The objective here is clear: to explore how yoga can be the game-changer in an athlete’s performance and flexibility. With regular practice, yoga can help athletes push their limits, recover faster, and achieve a level of harmony between mind and body that is often the difference between good and great.
The Science Behind Yoga and Athletic Performance
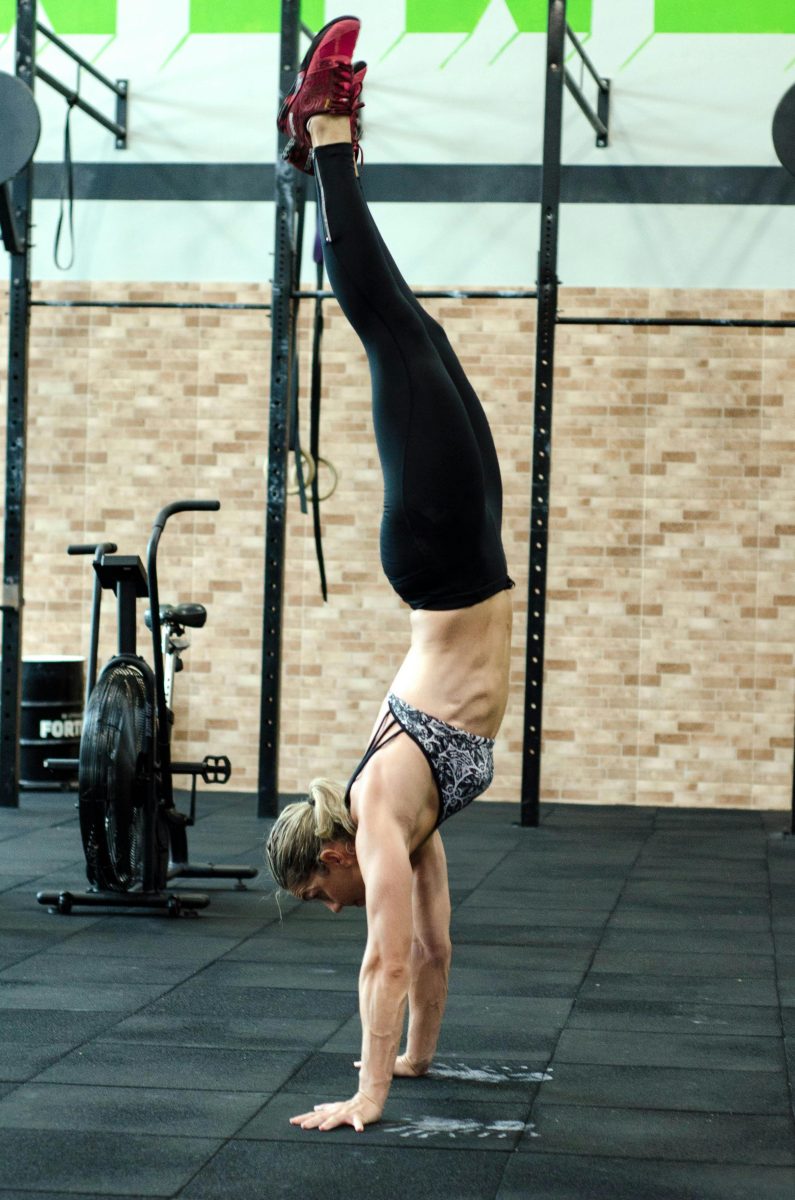
Understanding the Physiological Effects of Yoga on the Body
- Engaging in various poses stimulates the cardiovascular system, enhancing blood flow and oxygenation to muscles.
- Breathing techniques central to yoga practice improve lung capacity and efficiency, vital for athletes in managing their breath during intense physical exertion.
How Yoga Improves Muscle Strength, Endurance, and Flexibility
- Strength is not merely about muscle size but about the harmony and balance between muscle groups.
- Yoga promotes this balance, targeting often neglected muscles, thereby reducing the risk of injuries.
- The poses and stretches inherent to yoga practice are instrumental in enhancing flexibility, which in turn, contributes to a greater range of motion.
The Impact of Yoga on Mental Focus and Concentration
- The mental component of yoga encourages a mindfulness that sharpens focus and concentration.
- For athletes, this mental clarity can be the key to maintaining composure under pressure and making split-second decisions.
- The meditative aspects of yoga foster a sense of calm and resilience, enabling athletes to push through barriers with a centered and composed mindset.
Yoga Techniques for Enhanced Flexibility

The Importance of Flexibility in Athletic Performance
Flexibility is a cornerstone of athletic prowess, enabling athletes to execute movements with precision and ease. It reduces the risk of injuries by allowing muscles and joints to move through their full range of motion. Moreover, enhanced flexibility contributes to more efficient movements, saving energy and improving overall performance.
Specific Yoga Poses and Sequences for Athletes
- Pigeon Pose: Opens hip flexors and lower back, areas prone to stiffness.
- Downward-Facing Dog: Unmatched for improving hamstring and calf flexibility.
- Cobra Pose: For enhancing spine’s flexibility and strength.
Incorporating Dynamic and Static Stretching into Routines
- Dynamic stretching: Ideal at the beginning of a yoga session, preparing the body for physical activity.
- Static stretching: Best performed after a workout, helping in cooling down the body and promoting muscle recovery.
Strengthening the Body and Mind Through Yoga
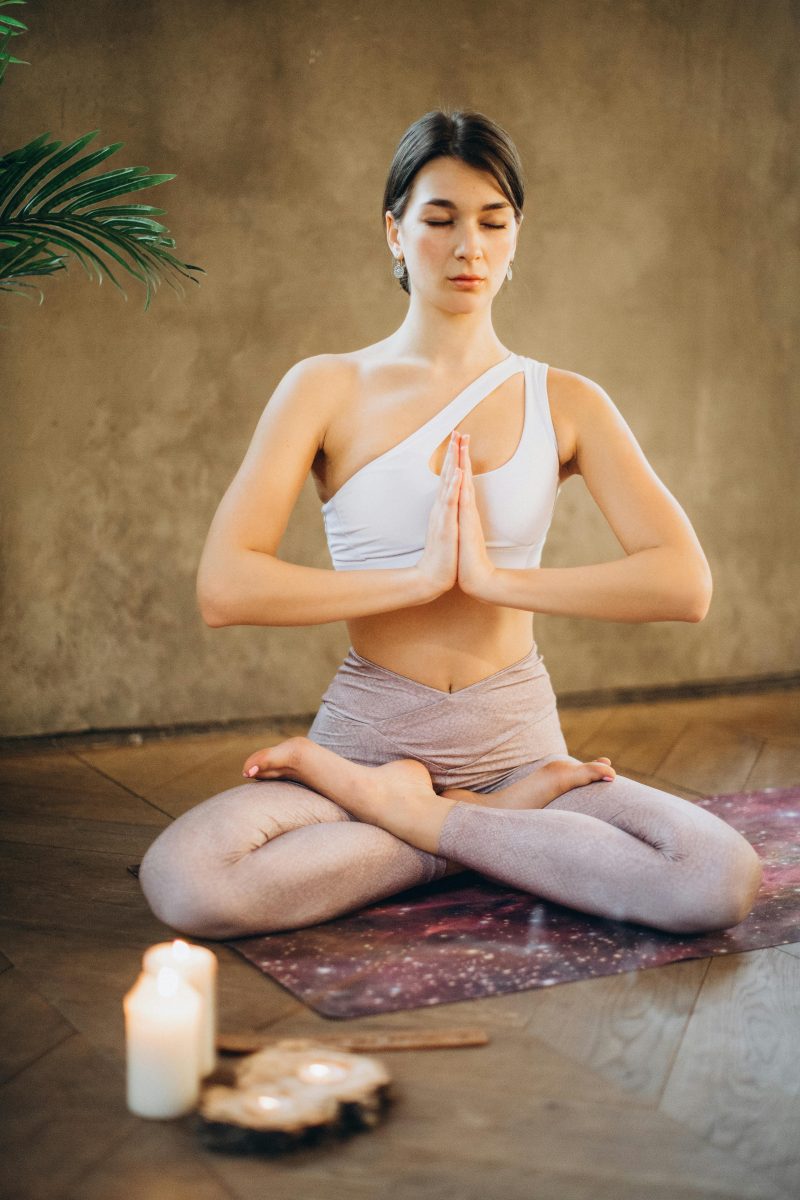

Yoga Poses That Build Strength in Key Muscle Groups for Athletes
- Warrior series: Enhances leg strength, stability, and stamina, crucial for runners and cyclists.
- Plank poses, including Side Plank: Fortify the core, shoulders, and arms, benefiting swimmers and climbers.
The Role of Yoga in Injury Prevention and Recovery
- Yoga’s emphasis on balance and flexibility plays a pivotal role in preventing injuries.
- For athletes in recovery, gentle yoga sequences aid in rebuilding strength and flexibility without overexertion.
Mental Resilience and Stress Reduction Through Mindful Yoga Practices
- Mindfulness cultivates mental resilience, enabling athletes to face challenges with composure.
- Practices such as deep breathing and meditation reduce stress levels, enhancing focus and performance under pressure.
Integrating Yoga into Athletic Training Regimens

Designing a Yoga Routine Tailored for Athletes
Creating a yoga routine for athletes starts with understanding the specific demands of their sport. Focus on poses that enhance core stability, balance, and flexibility, crucial for every athletic endeavor. Incorporate dynamic stretches to warm up and static stretches for cooling down, ensuring a comprehensive approach to training.
Balancing Yoga Practice with Traditional Athletic Training
Integrating yoga into an existing training regimen requires a balanced approach. Schedule yoga sessions on rest days or as a warm-up/cool-down routine. This ensures athletes reap the benefits of yoga, including improved flexibility and mental focus, without overtraining.
Tips for Beginners and Progressively Incorporating More Advanced Poses
Beginners should start with foundational poses, focusing on form and breath control. Gradually introduce more complex poses, paying attention to the body’s response. Encourage consistency and patience, as flexibility and strength build over time. Advanced poses, when approached methodically, can significantly enhance an athlete’s performance and recovery.
Yoga, with its unique blend of physical and mental training, offers athletes a competitive edge. By carefully integrating yoga into their training regimens, athletes can achieve a harmonious balance between strength, flexibility, and mental clarity, setting the stage for unparalleled performance and longevity in their sports careers.
Success Stories: Athletes Who Swear by Yoga

Testimonials from Top Performers
- LeBron James: NBA superstar who uses yoga to boost flexibility and mental focus.
- David Beckham: Credits yoga for career longevity and injury recovery in soccer.
Case Studies: Yoga’s Role in Athletic Transformation
- Rebecca Soni: Olympic swimmer who attributes success and stress management to yoga.
- Ryan Hall: Long-distance runner who improved running economy and reduced injuries with yoga.
These stories highlight the trend of athletes incorporating yoga into their training. They’ve experienced not just physical enhancements but also mental resilience boosts, showcasing yoga’s critical role in athletic performance.
In Closing
Yoga is the athlete’s secret weapon. It builds resilience and joy, enhancing both physical and mental performance. Through a blend of strength, flexibility, and mindfulness, yoga offers athletes a comprehensive tool for overcoming challenges and achieving peak performance. Success stories and scientific evidence underscore its transformative power, making it an essential component of athletic training. Let this be a call to action for athletes everywhere to embrace yoga, unlocking new levels of achievement and longevity in their sports careers.
Yoga for Athletes: Improving Performance and Flexibility FAQs
Yes, yoga can be an effective tool in both the prevention and rehabilitation of sports-related injuries. Through its emphasis on alignment, balance, and flexibility, yoga helps correct muscular imbalances and improve posture, which are common causes of injuries in athletes. Carefully selected poses can also aid in the recovery process by gently stretching and strengthening injured areas.
Yes, yoga can significantly improve your running performance by increasing flexibility, balance, and core strength. These improvements lead to better running form, reduced risk of injury, and enhanced endurance, enabling runners to train more effectively and efficiently. Additionally, the focus on breath work can improve oxygenation and energy management during long runs.
Yoga can effectively serve as both a warm-up and cool-down routine for athletes. Gentle yoga sequences can prepare the body for intense physical activity by increasing blood flow and flexibility, while slower, restorative yoga poses are ideal for cooling down and aiding in muscle recovery post-exercise. Incorporating yoga in this way ensures a holistic approach to training, addressing both physical and mental preparation and recovery.
Yoga improves an athlete’s breathing efficiency by teaching techniques that enhance lung capacity and control over breath. Practices such as pranayama (breath control exercises) train athletes to use their diaphragm fully, leading to increased oxygen uptake and better stamina. This improved breathing efficiency can significantly enhance performance, especially in endurance sports where breath management is key.
Yoga enhances flexibility, strength, and mental focus, crucial for athletes in any sport. By improving flexibility, yoga helps prevent injuries and promotes muscle recovery, allowing athletes to perform better and with greater longevity. The mental aspects of yoga, such as breath control and meditation, aid in concentration and stress management, directly impacting performance positively.
Yoga improves mental toughness by teaching athletes to remain focused, calm, and present under pressure. The practice of meditation and controlled breathing exercises helps in managing stress, anxiety, and distractions, which are crucial skills in competitive sports. This enhanced mental resilience translates into better performance during training and competitions.
Athletes should aim to practice yoga 2-3 times per week to gain significant benefits without overtraining. This frequency allows for sufficient recovery between sessions while providing ample opportunity to improve flexibility, strength, and mental focus. Tailoring the yoga routine to the athlete’s schedule and physical demands can optimize performance and recovery.
While yoga can be an effective component of an athlete’s strength training regimen, it typically should not be the sole method of strength training. Yoga practices, especially those that include poses like planks, warriors, and inversions, can build functional strength and muscular endurance. However, for maximum strength and muscle mass gains, incorporating weightlifting or resistance training is recommended.
Vinyasa or Ashtanga yoga are often considered the best types for athletes due to their dynamic and physically demanding nature. These styles focus on strength, flexibility, and endurance, offering a comprehensive workout that complements athletic training. Additionally, the breath synchronization with movement in these practices enhances cardiovascular fitness and mental focus.
Practicing yoga can affect your muscle mass by toning and strengthening muscles without necessarily increasing their size significantly. Yoga focuses on bodyweight exercises and endurance, which can lead to lean, strong muscles rather than the bulk created by weightlifting. However, when combined with resistance training, yoga can complement muscle growth by improving flexibility and reducing the risk of injury.
Orlando is a all round athlete from Australia, now resident in Germany. His sports of passion of American Football(Offensive line), weight training and indoor rock climbing where he uses his 195cm wing span to his advantage.



